Chapter - 3
Issue of Share
Chapter : 1 Introduction to Corporate Finance
Chapter: 2 Source of Corporate Finance
Chapter: 3 Issue of Shares
Chapter: 4 Issue of Debentures
Chapter: 5 Deposits
Chapter: 6 Correspondence with Members
Chapter: 7 Correspondence with Debenture holders
Chapter: 8 Correspondence with Depositors
Chapter : 9 Depository and Interests
Chapter : 10 Dividend and Interest
Chapter: 11 Financial Markets
Chapter: 12 Stock Exchange
__________________________________________________________________________________
Q.1 A) Select the correct answer from the options given below and rewrite the statements.
1. .................. refers to capital made up of Equity and preference shares
a) Share capital
b) Debt capital
c) Reserve fund
Ans: Share Capital
2. .................. capital refers to maximum capital a company can raise by issuing shares.
a) Issued
b) Authorised
c) Paid up
Ans: b) Authorised
3. .................. means shares are offered to the public.
a) Rights Issue
b) Private Placement
c) Public Issue
Ans: Public Issue
4. Under .................. method, issue price of shares is based on bidding.
a) Book Building
b) Fixed Price
c) Bonus Issue
Ans: Book Building
5. In .................., shares of a company are offered to the public for the first time.
a) Further Public Offer
b) Initial Public Offer
c) Public Offer
Ans: Initial Public Offer
6. .................. is offered to existing equity shareholders.
a) IPO
b) ESOS
c) Rights Issue
Ans: Right issue
7. Bonus shares are issued free of cost to .................. .
a) existing Equity shareholders
b) existing employees
c) Directors
Ans: a) Exiting Equity Share
8. .................. are offered to permanent employees, Directors and Officers of a company.
a) Bonus Shares
b) Rights Issue
c) ESOS
Ans: ESOS
9. Under .............., a company offers its securities to a select group of persons not exceeding 200.
a) Private Placement
b) IPO
c) Public Offer
Ans: Private Placement
10. The .................. have the power to allot shares.
a) Director
b) Board of Directors
c) Company Secretary
Ans: Board of Directors
11. Letter of .................. is sent to applicants who have been given shares by the company.
a) Regret
b) Renunciation
c) Allotment
Ans: Allotment
12. .................. is a proof of title to Shares.
a) Share Certificate
b) Register of Member
c) Letter of Allotment
Ans: Share Certificate
13. The gap between two calls should not be less than .................. .
a) 14 days
b) One month
c) 21 days
Ans: One month
14. Company can .................. shares on non-payment of calls.
a) forfeit
b) surrender
c) allot
Ans: a) forfeit
15. Voluntarily giving away one’s share to another person is called as .................. of shares.
a) Transfer
b) Transmission
c) Surrender
Ans: Transfers
16. .................. of shares takes place due to operation of law.
a) Forfeiture
b) Allotment
c) Transmission
Ans: Transmission
B. (I) Match the Pairs
|
Group
A |
Group
B |
||
|
a) |
Death of
member |
1 |
Forfeiture of
shares |
|
b) |
Voluntary
return of shares to company by member |
2 |
Book Building
Method |
|
c) |
Issue Price
of shares mentioned in prospectus |
3 |
Offered to
existing employees |
|
d) |
ESPS |
4 |
Surrender of
shares |
|
e) |
Regret Letter |
5 |
Transmission
of shares |
|
|
6 |
Non-allotment
of shares |
|
|
7 |
Offered to
existing Equity shareholders |
||
|
8 |
Transfer of
shares |
||
|
9 |
Fixed price
issue method |
||
|
10 |
Allotment of
shares |
||
Ans:
|
Group
A |
Group
B |
||
|
a) |
Death of
member |
5 |
Transmission
of shares |
|
b) |
Voluntary
return of shares to company by member |
4 |
Surrender of
shares |
|
c) |
Issue Price
of shares mentioned in prospectus |
9 |
Fixed price
issue method |
|
d) |
ESPS |
3 |
Offered to
existing employees |
|
e) |
Regret Letter |
6 |
Non-allotment
of shares |
B. (II) Match the Pairs
|
Group
A |
Group
B |
||
|
a) |
Issued Capital |
1 |
Non-payment
of calls |
|
b) |
FPO |
2 |
Any issue
after IPO |
|
c) |
Bonus shares |
3 |
Offered to
existing employees |
|
d) |
Issued within
two months of allotment of shares |
4 |
Capital
offered to public to subscribe |
|
e) |
Forfeiture of
shares |
5 |
Share
certificate |
|
|
6 |
First time
issue of shares |
|
|
7 |
Free shares
issued to existing equity shareholders |
||
|
8 |
Maximum
capital a company can raise |
||
|
9 |
Allotment
Letter |
||
|
10 |
Operation of
law |
||
Ans:
|
Group
A |
Group
B |
||
|
a) |
Issued Capital |
4 |
Capital
offered to public to subscribe |
|
b) |
FPO |
2 |
Any issue
after IPO |
|
c) |
Bonus shares |
7 |
Free shares
issued to existing equity shareholders |
|
d) |
Issued within
two months of allotment of shares |
5 |
Share
certificate |
|
e) |
Forfeiture of
shares |
1 |
Non-payment
of calls |
C) Write a word or a term or a phrase which can substitute each of the following statements.
1. Capital collected by way of issue of Equity and Preference shares.
Ans: Share Capital
2. Part of issued capital subscribed by investors.
Ans: Subscribe Capital
3. Capital that will be collected only at the time of winding up of a company.
Ans: Reserve Capital
4. Highest bid price in Book Building method.
Ans: Cap price Or Celling Price
5. Offering of shares by a company to the public for the first time.
Ans: Initial Public Offer
6. Subsequent issue of shares after an IPO.
Ans: Further Public Offer / Follow on Public Offer
7. Pre-emptive right given to existing Equity shareholders to subscribe to new issue of shares by company.
Ans: Right Share
8. It is also called as ‘Capitalisation of Profits’.
Ans: Bonus Share
9. Appropriation of shares to an applicant.
Ans: Allotment Share
10. Committee set up to decide the formula for allotment of shares in case of over subscription.
Ans: Allotment committee
11. Minimum amount to be collected from subscribers within thirty days of issue of prospectus.
Ans: minimum subscription
12. Document which is a prima facie evidence of ownership of certain shares of a company.
Ans: Share certificate
13. Penal action taken by company on non-payment of calls.
Ans: Forfeiture of share
14. Person to whom transferor is transferring the shares.
Ans: Transferee
15. Transfer of shares due to operation of law.
Ans: Transmission of share
D) State whether the following statements are true or false.
1. Only fully paid up shares can be forfeited.
Ans: False
2. The member transferring shares is called as transferor.
Ans: True
3. Share certificate is issued for partly or fully paid up shares.
Ans: True
4. Allotment of shares must be done within one month of receipt of application money.
Ans: False
5. Sweat Equity shares are offered to Directors or employees of a company.
Ans: True
6. Bonus Shares are issued at a discounted price to the Equity shareholders.
Ans: False
7. Floor price is the highest bid price under Book Building method.
Ans: False
8. Calls not paid by shareholder is called as calls in arrears.
Ans: True
9. Shares not offered to the public for subscription is called as subscribed capital.
Ans: False
10. Authorized capital is mentioned in capital clause of Memorandum of Association.
Ans: True
E) Find the odd one.
1. Authorized capital, Equity share capital, Issued capital, Paid-up capital.
Ans: Equity share capital
2. ESOS, ESPS, Rights Shares, Sweat Equity.
Ans: Rights Shares
3. Floor Price, Cap price, Cut-off price, Face Value.
Ans: Face Value
4. Bonus shares, Rights Shares, ESOS.
Ans: ESOS
5. Allotment of shares, Forfeiture of shares, Surrender of shares.
Ans: Allotment of shares
F) Complete the sentences.
1. Share capital refers to capital made up of Equity shares and .......................... .
Ans: Preference share
2. Reserve capital is part of .......................... .
Ans: Uncalled capital
3. Transfer of shares due to death, insolvency or insanity of member is called ...........................
Ans: Transmission of share
4. The two parties involved in transfer of shares are transferor and .......................... .
Ans: Transferee
5. Voluntarily giving up of shares by a member due to inability to pay calls is called as ..........................
Ans: Surrender of share .
6. Company can forfeit only .......................... paid shares.
Ans: Partly Paid Share
7. In case the original Share Certificate is torn or mutilated, company can issue ...........................
Ans: Duplicate share
8. In case of transfer of shares, company has to issue to the transferee a new share certificate within .......................... .
Ans: Month of date of receipt
9. Letter sent to applicants for informing them shares are allotted is called as ..........................
Ans: Letter of Allotment
10. When applications received are more than the number of shares offered, it is called as .......................... .
Ans: Subscription
11. In Book Building Method, the final price at which shares are offered to investors is called as .......................... .
Ans: Cut-off price
12. Shares issued free of cost to existing Equity shareholders is called as .......................... .
Ans: Bonus share
G) Select the correct option from the bracket
|
Group ‘A’ |
Group ‘B’ |
|
a) Public
Offer of share |
1) ----------- |
|
b) ------------------ |
2) Initial
Public Offer |
|
c) Right
issue |
3) --------------- |
|
d) ------------------ |
4) ESOS |
|
e) Operation
of law |
5) --------------- |
(First time offer of shares, Shares offered to public, Shares offered to existing Equity shareholders, Shares offered to existing employees, Transmission of shares)
Ans:
|
Group ‘A’ |
Group ‘B’ |
|
a) Public
Offer of share |
1) |
|
b) First time offer of shares |
2) Initial
Public Offer |
|
c) Right
issue |
3) Shares offered to existing Equity shareholders |
|
d)Shares offered to existing employees |
4) ESOS |
|
e) Operation
of law |
5) Transmission of shares |
H) Answer in one sentence.
1. When does transmission of share take place ?
Ans: Transmission of shares takes place due to operation of law i.e. the shares of a member are automatically transferred to another person on the death, insolvency or insanity of a member.
2. Name the parties involved in transfer of shares.
Ans: In transfer of shares
there are two parties involved- the member who is called as
transferor and the buyer who is called as transferee.
3. What is the time limit to
issue share certificate on allotment of shares ?
Ans: Within two months from the
date of issued certificate on allotment of share.
4. What is the time limit
for filing Return of Allotment with the Registrar on allotment of shares ?
Ans: The time limit for filing
Return of Allotment with the Registrar is of 30 days after the allotment of
shares
5. When can a company
forfeit shares ?
Ans: Company can forfeit the
shares if call money on shares are not paid by shareholder within stipulated
period.
6. What is a share
certificate ?
Ans: It is a registered
document issued by a company which is an evidence of ownership of specified
number of shares of the company.
7. What is the minimum
application money to be collected by company as per the Companies Act ?
Ans: Application money to be minimum 25% of the
nominal value of shares.
8. With whom should the
prospectus be filed before issuing it to the public ?
Ans: Prospectus should be filled with Register
of Companies (ROC) and stock exchange before issuing it to public.
9. What is meant by private
placement ?
Ans: Company offers its securities to a select
group of persons not exceeding 200. It is called private placement.
10. To whom is Sweat Equity
Shares offered by a company ?
Ans: Sweat Equity Shares
offered to its Directors or employees in recognition of their valuable
contribution to the company which has resulted in increased profits.
11. To whom can a company
issue Bonus Shares ?
Ans: company issue Bonus Shares to the existing
equity shareholders in proportion to their shareholding free of cost.
12. What is the subsequent
issue after IPO called as ?
Ans: Further Public Offer
or Follow on Public Offer (FPO) is the subsequent issue after IPO.
13. Name the method under
which the issue price of shares is fixed through a bidding process.
Ans: The method under which the issue price of
shares is fixed through a biding process called as 'Book Building Method'
14. What is Public Issue ?
Ans: Public Issue or offer
means offering the shares to the public.
15. Name the capital which
is mentioned in the capital clause of Memorandum of Association.
Ans: Authorized capital or Registered capital
is mentioned in the capital clause of Memorandum of Association.
I) Correct the underlined word/s and rewrite the following
sentences.
1. Issued capital is
the maximum capital which a company can raise by issuing shares.
Ans: Authorized
capital is the maximum capital which a company can raise by
issuing shares.
2. Under Fixed price
issue method, the price of shares is fixed through bidding
process.
Ans: Under book building method,
the price of shares is fixed through bidding process.
3. FPO refers
to offering of shares to the public for the first time.
Ans: IPO refers
to offering of shares to the public for the first time.
4. Only fully paid
up shares can be forfeited.
Ans: Only Partly paid
up shares can be forfeited.
5. Bonus shares are offered to
existing employees of a company.
Ans: Bonus shares are
offered to existing equity
shareholders of a company.
6. Company enters into an
underwriting agreement with the shareholders.
Ans: Company enters into
an underwriting agreement with the underwriters.
7. Letter of
Allotment is sent to applicants when no shares are allotted to
them.
Ans: Letter of regret is
sent to applicants when no shares are allotted to them.
8. Duplicate share certificate
must be issued within one month from date of
application.
Ans: Duplicate share
certificate must be issued within three month from date
of application.
9. Call money cannot
exceed 5% of nominal value of shares.
Ans: Call money cannot
exceed 25% of
nominal value of shares.
J) Arrange in proper order.
1. a) Forfeiture of shares.
b) Calls on shares.
c) Allotment of shares.
Ans:
c) Allotment of shares.
b) Calls on shares.
a) Forfeiture of shares.
2. a) Share certificate
b) Allotment letter
c) Application form
Ans:
c) Application form
b) Allotment letter
a) Share certificate
3. a) Return of allotment
b) Application form
c) Minimum subscription
Ans:
b) Application form
c) Minimum subscription
a) Return of allotment
Q.2 Explain the following terms/concepts:
Q.3 Study the following case/situation and express your opinion.
1. Eva Ltd. Company’s capital structure is made up of 1,00,000 Equity shares having face value of ` 10 each. The company has offered to the public 40,000 Equity shares and out of this, the public has subscribed for 30,000 Equity shares. State the following in `.
a) Authorised capital b) Subscribed capital c) Issued capital
Ans:
a) Authorized Capital:
Authorised capital = Equity shares X Face value of each share
Therefore, Authorised capital = 1,00,000 X 10 = 10,00,000
Authorised capital of Eva Ltd. is Rs. 10,00,000
b) Subscribed capital:
30,000 equity share of Rs. 10 each bought or subscribed by shareholders Hence, subscribed capital of the company is Rs. 3,00,000.
c) Issued capital:
The company has offered to the public 40,000 equity shares of Rs. 10 each. Therefore, issued capital is 4,00,000.
2. TRI Ltd. Company is newly incorporated public company and wants to raise capital by selling Equity shares to the public. The Board of Directors are considering various options for this. Advise the Board on the following matters :
a) What should the company offer - IPO or FPO ?
b) Can the company offer Bonus Shares to raise its capital ?
c) Can the company enter into Underwriting Agreement ?
b) Can the company offer Bonus Shares to raise its capital ?
3. Silver Ltd. Company has recently come out with its public offer through FPO. Their issue was over subscribed. The Board of Directors now wants to start the allotment process. Please advise the Board on :
a) Should the company set up allotment committee ?
b) How should the company inform the applicants to whom the company is allotting shares ?
c) Within what period should the company issue share certificate ?
Ans:
a) Should the company set up allotment committee?
Yes, Silver Ltd. company should immediately call the Board Meeting and appoint an Allotment committee and gives them power to decide the policy of allotment of shares. Then the Allotment Committee will decide the basis of allotment and submit a report to the Board.
b) How should the company inform the applicants to whom the company is allotting shares ?
Silver Ltd. Company should instruct the secretary to send letter of allotment to the applicant to whom shares are allotted and to send letter of regret along with refund order to whom shares are not allotted.
c) Within what period should the company issue share certificate ?
Silver Ltd. Company should issue shares certificates to the shareholders within 60 days (two months ) of allotment of shares.
4. Red Tubes Ltd. has made a demand on its shareholders to pay the balance unpaid amount of ` 20/- per share (having a face value of ` 100) held by them. The company has sent letters asking the shareholders to pay the money to its Bankers within the specified time.
a) Are the shareholders liable to pay ` 20 for the shares held by them ?
b) Name the letter sent by the company to its shareholders asking them to pay ` 20/-
c) What happens if a shareholder fails to pay the money within the specified time ?
Ans:
a) Are the shareholders liable to pay ` 20 for the shares held by them ?
The unpaid amount on partly paid up shares its a liability of the shareholder. Thus, shareholders are liable to pay 20 for the shares held by them when demanded by the company.
b) Name the letter sent by the company to its shareholders asking them to pay ` 20/-
The letter sent by the company to its shareholders asking to pay Rs. 20 is called as 'Call Letter' and the reminder for the same is called as 'Call Reminder'.
c) What happens if a shareholder fails to pay the money within the specified time ?
If shareholders fall to pay the call money within the specified time, his shares are liable to be forfeited and his name can be removed from the register of members.
5. X owns 100 shares while Y owns 500 shares of Red Tubes Ltd. The company has asked all its shareholders to pay the balance unpaid amount of ` 20. X pays the full money demanded by the company. Y, who is in a bad financial position is unable to pay any money.
a) Can the company forfeit the shares of Y ?
b) Can the company forfeit the shares of X ?
c) Can X transfer his shares ?
Ans:
a) Can the company forfeit the shares of Y ?
The unpaid amount on partly paid up shares is a liability of the shareholder, If the shareholder fails to pay the calls, company can forfeit the shares. so Red Tubes Ltd. can forfeit the share of Y.
b) Can the company forfeit the shares of X ?
NO, Red Tubes Ltd. company can't forfeit the shares of X as X has already paid the full money demanded by company. Also, fully paid up shares cannot be forfeited.
c) Can X transfer his shares ?
Every member has a right to transfer their shares. Mr. X shares are fully paid up and fully paid shares are easily transferable. so, Mr, X has to apply to the company for transfer of shares by filling the 'Instrument of Transfer' and submit the share certification along with the required transfer fees.
Q.4 Distinguish between the following.
1. Initial Public Offer and
Ans:
|
|
Initial
Public Offer |
Further
Public Offer |
|
|
1.meaning |
IPO refers to an
offer of securities by an unlisted Public Company to the public for the first
time. |
FPO means an
offer of securities by a listed Public Company to the public to raise
subsequent capital. |
|
|
2. Types
of issuer company |
It is issued by
an unlisted Public Company. |
It is issued by
a listed Public Company. |
|
|
3.
when issue |
It is usually
issued by an existing company which wants to raise capital from the public
for the first time. |
It is usually
issued by a listed Public company when it wants to raise further capital from
the public. |
|
|
4.
order of issue |
IPO preceeds
FPO. IPO is the first-time sale of shares to the public. |
FPO is always
done after IPO. FPO is the second or subsequent sale of shares to the public. |
|
|
5.
Listing |
Company has to
get itself listed for the first time before issuing IPO. |
Company making
an FPO is already a listed company |
|
|
6.
Risk |
It is very risky
for the investor as he cannot predict the company’s performance. |
It is less risky
for the investor as he has an idea of the company’s past performance and can
judge its future performance. |
|
2. Fixed Price Issue and Book Building
Ans:
|
|
Fixed
Price Issue |
Book
Building |
|
1.meaning |
Under this
method, the issue price of shares is mentioned in the prospectus and
investors have to buy shares at that price only |
Under this
method, the issue price is determined by a bidding process. The investors are
given a price band and are asked to bid at a price within the band. This way
company arrives at a price at which it will sell its shares. |
|
2.Price
of share |
The exact price
of shares is known in advance and it is mentioned in the prospectus |
The price of
shares is not known in advance. Only the minimum price and maximum price at
which the company is willing to sell the shares is known in advance. |
|
3.
Prospectus |
Company has to
issue a prospectus and it contains the details of price at which shares are
offered and the total number of shares offered by the company. |
Company issues a
Red Herring Prospectus. It contains only the price band and the total size of
issue |
|
4.
Determination of Demand |
Company comes to
know the public demand for its shares only after closure of the issue |
Company can know
the public demand for its shares everyday. The bids are registered in the
book everyday till the closure of the issue |
|
5.
Payment of Application money |
Application
money or entire money has to be paid by the investor at the time of
submitting his application for shares. |
Only application
money has to be paid at the time of bidding. Money will be collected only
after the issue price has been fixed. |
|
6.
when used |
It can be used
for any issue i.e. Public Issue, Rights Issues, ESOS, etc. |
It is usually
used in Public issues i.e. IPO and FPO. |
3. Rights Shares and Bonus Shares
Ans:
|
|
Right Issue |
Bonus Share |
|
1.meaning |
In rights issue,
shares are offered to the existing equity shareholders i.e. Company offers the
shareholders the first option to buy the shares of the company. |
Bonus shares are
issued to the existing equity shareholders free of cost. |
|
2.
Payment |
Subscribers have
to pay for the Rights Shares. Company only gives them a right to buy these
shares. |
Bonus shares are
issued free of cost to the shareholders. |
|
3. Partly / fully
paid up shares |
Shareholders
have to pay for these shares as Application Money, Allotment, Call Money etc.
till the full money on shares is paid up |
Bonus shares are
fully paid up shares. So no money has to be paid by the shareholders to the
company |
|
4. Minimum
Subscription |
Company has to
obtain minimum subscription. If the company fails to receive minimum
subscription, it has to refund the entire application money received. |
There is no
minimum subscription to be collected as Bonus shares are issued free of cost
by the company |
|
5. Right to
Renounce |
The shareholders
can renounce his shares. |
Shareholders
cannot renounce his bonus shares |
|
6. Purpose of Issue |
Rights issue is
done by a company when it wants to raise fresh funds but wants to give a
chance to their existing members to increase their shareholding. |
When company has
accumulated huge profits or reserves and company wants to reward its existing
Equity shareholders, company issues Bonus shares. |
4. Transfer of Shares and Transmission of Shares
Ans:
|
|
Transfer
of Shares |
Transmission
of Shares |
|
1,
meaning |
Transfer of
shares means voluntarily or deliberately giving away one’s shares to another
person by entering into a contract with the buyer. |
It means
transfer of ownership of a member’s shares to his legal representative due to
operation of law. It takes place on death, insolvency or insanity of the
members |
|
2. When done |
It is done when
the member wants to sell his shares or give his shares as gift. |
It is done when
the member dies or becomes insolvent or insane |
|
3. Nature of Action |
It is a
voluntary action taken by the member |
It is an
involuntary action. It is due to operation of law |
|
4. Parties involved |
In transfer of
shares there are two parties involved- the member who is called as transferor
and the buyer who is called as transferee. |
There is only
one party e.g. the nominee of the member in case of death of the member or
the legal representative |
|
5. Instrument of
transfer |
Transfer
requires Instrument of transfer. It is a contract between the transferor and
transferee. |
No Instrument of
transfer is needed. |
|
6. Initiated by |
Transferor
initiates the transfer process. |
Legal
representative or official receiver initiates the process of transmission |
|
7. Consideration |
Transfer of
shares is done often by the member to receive some consideration (money) i.e.
the buyer has to pay for the shares. (Except given as gift.) |
No consideration
is involved here. The legal heir or official receiver need not pay for the
shares. |
|
8.
Liability |
The liability of
the transferor ends after the shares are transferred. |
Original
liability of the member continues in case of transmission of shares |
|
9. Stamp Duty |
Stamp duty as
per the market value of shares has to be paid. |
No stamp duty is
to be paid |
Q.5 Answer in brief.
1. What is Book Building Method ?
Ans: i) Under this method, the issue price is determined by a bidding process. The investors are given a price band and are asked to bid at a price within the band. This way company arrives at a price at which it will sell its shares.
ii) The price of shares is not known in advance. Only the minimum price and maximum price at which the company is willing to sell the shares is known in advance.
iii) Company issues a Red Herring Prospectus. It contains only the price band and the total size of issue.
iv) Company can know the public demand for its shares everyday. The bids are registered in the book everyday till the closure of the issue.
v) Only application money has to be paid at the time of bidding. Money will be collected only after the issue price has been fixed.
vi) It is usually used in Public issues i.e. IPO and FPO.
2. State the provisions for Rights Issue.
Ans:
Provisions : Company making Rights Issue has to fulfill the following provisions.
a) Rights shares are sold to the existing shareholders at a price which is lesser than its market price.
b) A company has to send ‘Letter of offer’ to the existing shareholders at the time of issuing Rights shares.
c) The letter of offer shall mention : i) the number of shares offered
ii) the period of offer i.e. offer is valid for a period not less than fifteen days and not exceeding thirty days from the date of offer.
iii) the right to renounce i.e. the shareholders have a right to give up their shares in favour of any other person.
d) The letter of offer can be sent by registered post, speed post, courier or through electronic mode.
e) If a shareholder does not respond to the Rights Issue offer within the stipulated time, it is implied that he is not interested in the offer and the company can offer the unsold shares to new investors.
3. State the provisions related to Bonus Shares.
Ans:
Provisions : Following are the provisions related to Bonus Issue
a) A company can issue Bonus Shares only out of :
i) Free reserves or
ii) Securities Premium Account or
iii) Capital Redemption Reserve Account
b) A company cannot issue Bonus shares out of reserves created by Revaluation of Assets
c) It also cannot issue Bonus Shares instead of paying dividend.
d) Once the announcement for Bonus Shares is made by the Board of Directors, it cannot be then withdrawn.
e) Bonus shares are fully paid up shares.
f) Shareholders cannot renounce i.e. give away their Bonus shares to another person.
g) There is no minimum subscription to be collected.
4. State the general principles / rules for allotment of shares.
Ans:
These are rules that a company must follow in addition to the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013.
(1) Proper Authority : The Board of Directors or the allotment committee set up by the Board has the authority to allot shares.
(2) Allotment must be against application only : A company can allot shares only if it has received a written application for shares from the applicant.
(3) Reasonable time : As per the Act, allotment shall be done within 60 days of receipt of application money. Allotment can be made from the fifth day from date of issue of prospectus.
(4) Absolute and Unconditional allotment : Shares should be allotted on the same terms as stated in the prospectus and application form. No change in the terms of allotment or new conditions can be added at the time of allotment.
(5) Communication : Company has to inform the applicant that shares have been allotted to him by sending a letter of allotment or allotment advice. This letter gives details of number of shares allotted, amount of Allotment money to be paid, etc.
(6) Allotment should not be in contravention (violation) of any other laws : A Company cannot allot shares by violating or contradicting any other existing laws. e.g. Shares cannot be allotted to a minor.
5. State the contents of Shares Certificate.
Ans:
It is a registered document issued by a company which is an evidence of ownership of specified number of shares of the company. Share certificate is a prima facie evidence of title to shares.
Contents of Share Certificate : Share certificate should be in Form SH-1 as prescribed under Companies (Share Capital and Debenture) Rules, 2014. Following are the contents of a share certificate __ i) Name of the Company, CIN, Registered office address. ii) Folio Number iii) Share Certificate Number iv) Name of Member v) Nature of share, number of shares and distinctive number of the shares. vi) Amount paid on shares vii) Common Seal, if any and signature of two Directors and Company Secretary.
6. What are the effects of forfeiture of shares ?
Ans:
If a shareholder fails to pay calls on shares within a certain period, the Board of Directors, if authorised by the Articles of Association, can forfeit i.e. take away the ownership of a member. This is called as forfeiture of shares. Only partly paid up shares can be forfeited.
Effects of forfeiture i) Cessation of Membership : On forfeiture, a member ceases to be member of a company and loses all membership rights. The member’s name is removed from the Register of Members. ii) Liability of member : A member is liable for unpaid calls even after forfeiture of shares. The liability ceases only when the company reissues the forfeited shares. iii) Liquidation of company : If a company goes in for liquidation within one year of forfeiture of shares, the member whose shares have been forfeited is liable to pay the calls as a past member.
7. When can the Board of Directors refuse transfer of shares ?
Ans: when a member voluntarily transfers shares to another person for monetary reasons or gives it as a gift to another person.
Refusal to transfer shares :
Board of Directors has the authority to refuse registration of transfer of shares. A notice of refusal giving the reasons for refusing transfer by the Board is to be sent to the member within thirty days from the date on which the Instrument of transfer was delivered to the company.
The Board may refuse registering the transfer under following conditions :
i) When the provisions for transfer of shares as given in the Articles of Association is not fulfilled by the member.
ii) When the instrument of transfer is not as per the rules prescribed under the Companies Act.
iii) When the Instrument is not accompanied by the Share Certificate.
iv) When the company has a lien on the shares to be transferred. A member may appeal to the NCLT against the refusal by the Board within a period of thirty days from date of receipt of refusal notice. If no notice is received, the member can appeal within 60 days in case of a Private Company and within 90 days in case of a Public Company.
8. Explain Employee stock option scheme.
Ans: Under this scheme, permanent employees, Directors or officers of the company or its Holding Company or Subsidiary company are offered the benefit or right to purchase the Equity Shares of the company at a future date at a pre-determined price.
ESOS encourages employees as they feel proud to be owners of the company for which they are working and company also benefits as it can retain good employees.
a) A company may offer the shares directly to the employees or through an Employee Welfare Trust.
b) The shares are offered at a price lesser than their market price.
c) There is a minimum vesting period of one year.
d) Usually company will specify the lock-in period i.e. period during which employee cannot sell his shares. Lock-in period is minimum 1 year.
e) Shares issued under this scheme do not enjoy any dividend or voting rights till the employee buys the shares.
f) Company has to get the approval of shareholders through special resolution to issue ESOS.
g) Employee cannot transfer his option to any other person nor can he pledge or mortgage the shares issued under ESOS
9. What is calls on shares ?
Ans: At the time of issue of shares, a company may state that the issue price of the shares is to be paid in instalments as and when the company demands for it. So when a company demands the shareholder to pay a part or full amount of the balance amount unpaid on shares, it is called as ‘Calls on Shares’.
Thus, besides the application money and allotment money, if a company demands the balance unpaid amount on shares, it is called as calls on shares. The unpaid amount on partly paid up shares is a liability of the share holder.
If the shareholder fails to pay the calls, company can forfeit the shares. Calls can be made only by the Board of Directors in the interest of the company.
Company has to send a call letter/notice to the shareholders asking them to pay the call money and give them minimum 14 days notice to pay the call money to the Company’s Banker. No call can be made for more than 25% of the nominal value of shares.
10. What is transfer of shares ?
Ans:
i) Transfer of shares means voluntarily or deliberately giving away one’s shares to another person by entering into a contract with the buyer
ii) It is done when the member wants to sell his shares or give his shares as gift.
iii) It is a voluntary action taken by the member.
iv) In transfer of shares there are two parties involved- the member who is called as transferor and the buyer who is called as transferee.
v) Transfer requires Instrument of transfer. It is a contract between the transferor and transferee.
vi) Transferor initiates the transfer process.
vii) Transfer of shares is done often by the member to receive some consideration (money) i.e. the buyer has to pay for the shares. (Except given as gift.)
viii) The liability of the transferor ends after the shares are transferred.
ix) Stamp duty as per the market value of shares has to be paid.
Q.6 Justify the following statements.
1. Company has to fulfill certain provisions while making Right Issue.
2. To Issue Bonus Shares, a company has to fulfill certain provisions.
3. ESOS is offered by a company to its permanent employees, Directors and Officers.
4. Company has to fulfill general principles/rules for allotment of shares.
5. A company can issue duplicate share certificate.
6. Board of Directors have the authority to forfeit shares.
7. A member of a Public company can transfer shares.
8. The Board of Directors can refuse transfer of shares.
Q.7 Answer the following questions.
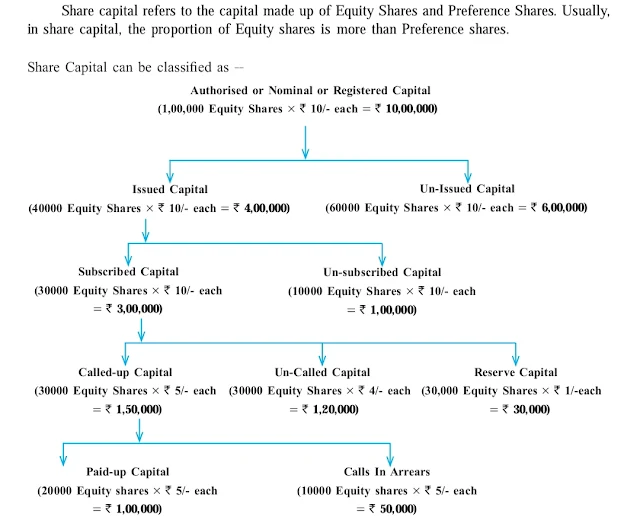
1. Explain the classification of share capital.
Ans:
A. Authorised/Nominal or Registered Capital :
Authorised Capital is the maximum capital authorised by Memorandum of Association that a company can raise by issuing shares. It is also called as Registered Capital as it is mentioned in the capital clause of Memorandum of Association and the company pays stamp duty on this amount at the time of incorporation. Authorised Capital is calculated considering the need of capital of a company at present and in future.
Authorised Capital is also called as Nominal Capital as usually a company never issues the entire Authorised Capital.
e.g. ‘M’ Ltd. Company has Authorised Capital of ` 10,00,000 which can be divided into 1,00,000 Equity shares having a face value of ` 10 each.
A company can increase its Authorised capital by altering its Memorandum of Association.
B. Issued and Unissued Capital :
Issued Capital is that part of Authorised Capital which is offered by the company to prospective investors for subscription. Thus, it is the shares that the company is offering to the public to buy.
The balance part of Authorised capital not offered to the public is called as ‘Unissued Capital’. In future, the company can issue shares from the unissued capital. The issued capital of a company may be equal to or less than the Authorised Capital.
e.g. ‘M’ Ltd. Company can have Issued Capital of ` 4,00,000 divided into 40,000 Equity shares at face value of `10/- each and the unissued capital will be ` 6,00,000 divided into 60,000 Equity shares of ` 10/- each.
C. Subscribed and Unsubscribed Capital :
Subscribed capital is that part of Issued-capital which has been subscribed or taken up (bought) by investors (subscriber). The public may or may not subscribe for the entire Issued capital. Hence, that part of the Issued capital not subscribed by the investors is called as ‘unsubscribed capital’. Thus, the subscribed capital may be equal to or less than the Issued capital.
e.g. If ‘M’ Ltd. Company has Issued capital of ` 4,00,000 i.e. has issued 40,000 Equity shares, then the company’s subscribed capital can be ` 3,00,000 divided into 30,000 Equity shares of ` 10/- each. Hence, the unsubscribed capital will be ` 1,00,000 divided into 10,000 Equity shares of ` 10/- each.
D. Called-up Capital, Uncalled Capital and Reserve Capital :
At the time of Issue, full value of the shares is usually not demanded by the company. Company collects the full value of shares in instalments as per its requirement of funds. Each Instalment is called as ‘calls’. Called-up capital is that part of subscribed capital which a company has ‘called’ or demanded to be paid by the shareholders. The balance capital which is not demanded from the shareholders is called as uncalled capital.
Reserve Capital is a part of uncalled capital. A company can decide to keep aside a part of its uncalled capital to be called up only at the time of winding up of a company to meet its financial requirements.
e.g. ‘M’ Ltd. Company may have called up capital of ` 1,50,000 i.e. 30,000 Equity shares of face value of ` 10/- each out of which ` 5/- per share has been called up/demanded by the company.
If the company decides to keep Re. 1/- per share as capital to be collected at the time of the winding up, the Reserve Capital will be ` 30,000 i.e. 30,000 equity shares of ` 10/- each where Re. 1 per share is kept as Reserve Capital.
Uncalled capital will be ` 1,20,000 i.e. 30,000 Equity shares where ` 4 per share which will be called up in future.
E. Paidup Capital and Calls in Arrears :
Paid up capital is the total amount of money actually paid up by the shareholders when the company has called up or demanded them to pay. The amount not paid up by the shareholders is called up as Calls in Arrears or unpaid calls.
2. Explain the two methods a company can use to make its public offer of shares.
Ans: (A) Public Issue or Public offer of Shares : Public Issue or offer means offering the shares to the public. This is the most common method used by companies. The company invites the public to subscribe for its shares by issuing prospectus.
A company can use two pricing methods to offer shares to the public Under this method, the issue price of shares is mentioned in the prospectus and investors have to buy shares at that price only.
The exact price of shares is known in advance and it is mentioned in the prospectus.
3. Explain briefly the different types of shares offered by a company to its existing Equity shareholders.
4. Explain the statutory provisions for allotment of shares.
5. Explain briefly the procedure for allotment of shares.
1. | Choose the Correct Option | 5 Marks | |
2 | Complete the Correction | 5 Marks | |
3 | Give Economic Term | 5 Marks | |
4 | Find the Odd Word | 5 Marks | |
5 | Complete the following Statements | 5 Marks | |
6 | Assertion and Reasoning Questions | 5 Marks | |
7 | Identify and Explain the Concepts | 6 Marks | |
8 | Distinguish Between | 6 Marks | |
9 | Answer in Brief | 12 Marks | |
10 | State with Reasons, Do you Agree/ Disagree | 12 Marks | |
11 | Table, Diagram, Passage Based Questions | 8 Marks | |
12 | Answer in Detail | 16 Marks |



.png)
.png)
0 Comments